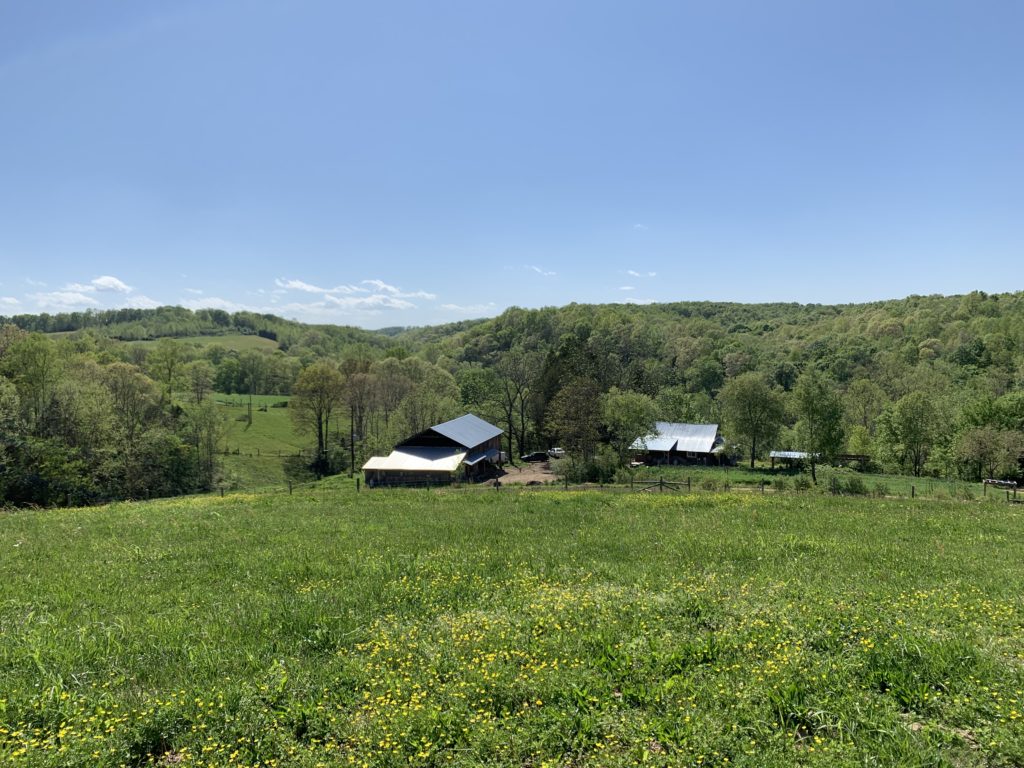
Biodynamic farming is defined by the Biodynamics Association as a holistic, ecological, and ethical approach to farming, gardening, food, and nutrition. The practice of biodynamic farming was first introduced in the 1920’s by Dr. Rudolf Steiner, a philosopher and scientist, as an alternative to farming that relied on chemical fertilizers. Farmers sought Dr. Steiner’s advice for alternatives as they saw declines in soil health and crop yields.
Biodynamics take the principles of organic farming and goes one step further. The approach views the farm as it’s own self-sustaining, biodiverse organism. A biodynamic farmer takes into consideration not only the physical environment, but also universal energy that affects the plants growth, nutrition and health.
A biodynamic farm employs natural methods for renewing soil nutrients, repelling harmful pests and attracting beneficial insects. The farmers make their own compost with materials naturally occurring on the farm. Cover crops and crop rotation are other tenants of biodynamic farming; intentionally choosing plants for their ability to replenish soil with nutrients.
Companion planting is another practice used by biodynamic farmers. Companion planting is when two plants are planted in close proximity to each other because they have the ability to benefit from each other. A home garden example featured on The Spruce, basil, borage, chives and nasturtium are a few companion plants that will help your tomatoes thrive, each for a different reason. Lastly, the phases of the moon, planets and stars guide the activities on a biodynamic farm.
You may be wondering why soil is such a big part of the farming conversation, it’s just dirt right? Healthy soil supplies plants with essential nutrients, beneficial bacteria and moisture. Monoculture lacks diversity and inherently requires the use of chemicals. Shirking the reliance on chemical fertilizers, biodynamic practices use the previously mentioned methods to keep their soil balanced. The result is healthy, well producing plants.
How can you tell if produce is biodynamic? In the supermarket, there is a biodynamic certification offered by Demeter USA which will indicate a product was produced on a certified biodynamic farm. As with any certification, they can be quite costly for small, independent farmers. The best way to understand a farmers principles and practices is to ask them. Shopping your local farmer’s market gives you direct access to the people growing your food. It allows for an open dialogue where you can get to know your farmer and understand their specific approach to farming.
The cornerstone of biodynamic farming is the self-sustaining ecosystem ideology. Biodynamic farming combines scientific practices with the rhythms of nature. It encourages healthy and natural biodiversity, rather than a monoculture managed by chemical sprays. Biodynamic farming is a holistic approach to growing food and raising animals.
Although controversial, there are studies that have shown that organic and biodynamic farming practices results in more nutrient dense food. Of course conventional farmers object vehemently to this type of statement being made. I urge you to consider the practices used in biodynamic farming to make your own common sense decision about which type of agriculture you want to support and nourish yourself with.